How to begin your Lean Journey?
- By Brett Griffiths
- Lean Technology
- August 14 , 2023
- Share
Lean Manufacturing, is not just a passing trend; it's a proven philosophy that has revolutionised industries across the globe. At its core, lean is about maximising value while minimising waste. It empowers manufacturers to streamline processes, enhance productivity, and deliver top-notch products or services to their customers, all while minimising costs and environmental impact.
Implementing Lean principles is not a "one-size-fits-all" approach. Instead, it's a mindset that encourages continuous improvement and a commitment to identifying and eliminating inefficiencies throughout production. Manufacturers can achieve enhanced operational efficiency, reduced lead times, increased product quality, and a more engaged and motivated workforce by adopting lean methodologies.
Let's move on to a journey where you will discover the basics of lean Manufacturing. We will also discuss practical steps that you can take to start your lean transformation journey.
What does "Lean" mean in Business?
Lean represents a management philosophy and operational approach aimed at maximising efficiency, minimising waste, and delivering value to customers. Originating as the Toyota Production System (TPS) in the 1950s, lean has gained global adoption, proving its effectiveness in enhancing competitiveness. By embracing lean principles, businesses can optimise their processes, eliminate inefficiencies, and remain customer-focused, creating a solid connection between lean implementation and achieving a competitive edge in the market.
Lean is centred around the lean principles, which form the foundation of this management philosophy.
- Value: Identifying what the customer perceives as valuable in the product or service. Value is any activity that meets the customer's needs or requirements.
- Value Stream: Mapping the entire value stream, representing all the steps and processes involved in delivering a product or service from its inception to the customer's hands.
- Flow: Ensuring the value stream flows smoothly without interruptions, avoiding bottlenecks and delays.
- Pull: Using a pull-based system to produce what the customer demands, reducing excess inventory and overproduction.
- Perfection: Striving for continuous improvement in all aspects of the operation, seeking perfection, and making incremental changes to eliminate waste and enhance efficiency.
The primary goal of lean in various sectors is to create more value for customers while minimising waste and non-value-adding activities. In the lean context, waste refers to any activity or resource that does not contribute to creating value for the customer. Check out this link for more information on identifying and eliminating 8 lean wastes.
How do you start your Lean Manufacturing Journey?
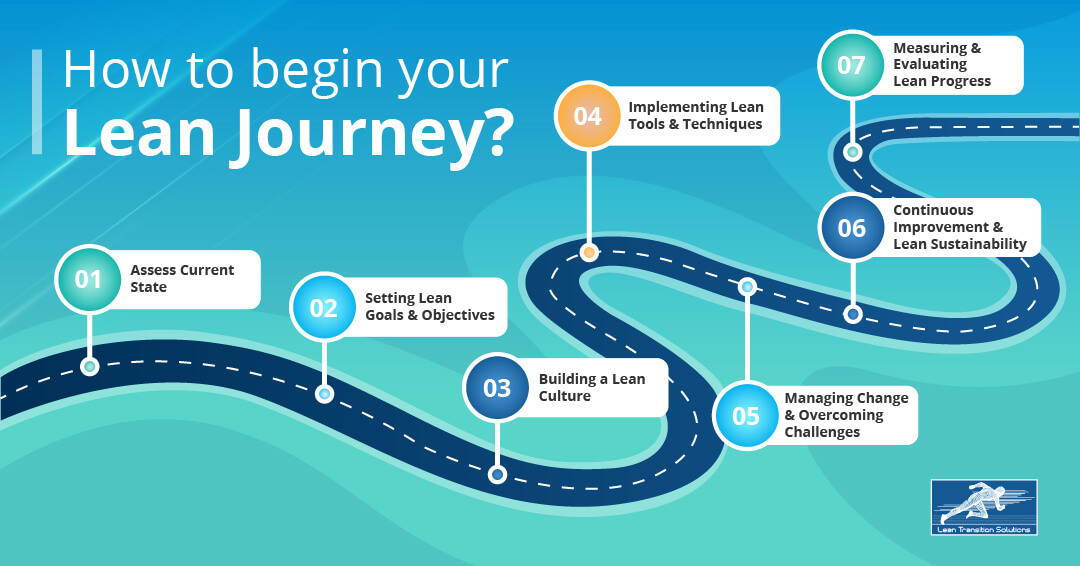
Step 1: Assess Current State
Conducting a lean assessment helps organisations evaluate their readiness and capability to adopt lean methodologies. By identifying improvement areas, companies can pinpoint specific processes that require optimisation and waste reduction. Analysing existing processes and workflows allows organisations to gain insights into current operations and identify bottlenecks or inefficiencies. This comprehensive assessment sets the stage for a successful lean transformation, enabling businesses to make informed decisions and strategically implement changes that will drive continuous improvement and operational excellence.
Step 2: Setting Lean Goals and Objectives
Setting lean goals and objectives is a crucial step in the lean journey. Clearly defining objectives ensures a focused direction for improvement efforts. By establishing Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), progress can be measured effectively, providing valuable insights into the success of lean initiatives. Aligning lean goals with overall business objectives ensures that improvements contribute directly to the organisation's strategic success. With well-defined objectives, measurable KPIs, and alignment with business goals, lean implementation becomes purposeful and drives significant positive organisational change.
Step 3: Building a Lean Culture
To build a lean culture, start by fostering a shared vision and commitment to continuous improvement at all levels of the organisation. Engage employees in lean training and provide them with the tools and resources to identify and eliminate waste in their processes. Encourage open communication and empower teams to make data-driven decisions. Implement Visual management techniques to enhance transparency and promote accountability.
Step 4: Implementing Lean Tools and Techniques
As you embark on your lean journey, implement Lean tools and techniques effectively. Start by introducing common Lean tools such as 5S, Kaizen events, Value Stream Mapping, Kanban system, and Poka-yoke (error-proofing). Then, carefully assess your organisation's needs and processes to choose the right tools that align with your objectives. Finally, invest in training employees on these lean tools and methodologies to ensure their understanding and active participation in the continuous improvement process. It allows you to lay a strong foundation for a successful lean implementation that optimises processes, eliminates waste, and fosters a culture of excellence throughout your organisation.
Step 5: Managing change and overcoming challenges
To successfully implement lean practices, it is important to address any resistance to change and effectively communicate the benefits of lean to stakeholders. You can start by identifying potential sources of resistance and addressing concerns through open dialogue and transparent communication. Encourage stakeholder engagement by highlighting the positive impact of lean on productivity, quality, and customer satisfaction. Empower employees with training and the opportunity to participate in decision-making processes, which fosters a sense of ownership and commitment. Emphasise the long-term benefits of lean, including reduced waste, increased efficiency, and a competitive edge. Organisations can overcome challenges and achieve successful implementation by fostering a shared understanding and enthusiasm for lean principles.
Step 6: Continuous Improvement and Lean Sustainability
To effectively apply lean principles, it is crucial to establish a continuous improvement system and guarantee that the organisation can maintain lean practices in the long run. This involves creating a culture that promotes learning from both successes and failures. By encouraging employees at all levels to share insights, identify improvement opportunities, and implement solutions, lean becomes an ongoing practice. Regularly reviewing processes, gathering feedback from customers and employees, and adapting to changing market conditions are integral to sustaining lean principles. By embracing this approach, companies can maintain their lean journey's momentum, adapt to evolving needs, and continually enhance efficiency, quality, and customer value.
Step 7: Measuring and evaluating Lean Progress
A lean journey isn't complete without measuring and evaluating progress using data-driven metrics. Organisations can objectively assess lean success by establishing clear and relevant Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). Regular performance reviews and assessments provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of lean initiatives. Analysing data allows teams to identify areas of improvement and make informed, data-backed decisions to optimise processes further. By focusing on data-driven evaluation, organisations can continually refine their lean strategies and ensure continuous improvement throughout the entire lean journey.
Keeping up with Lean trends
- Exploring emerging Lean practices and technologies: As lean principles continue to evolve, it's essential for organisations to keep up with the latest trends and practices. Exploring emerging lean methodologies and technologies allows businesses to identify innovative approaches to streamline processes, reduce waste, and improve asset efficiency. Staying up-to-date with the latest advances in industrial automation, data analytics, Artificial Intelligence (AI), and digital tools can give organisations the power to take advantage of new opportunities and remain competitive in today's industrial landscape.
- Adapting Lean principles to changing business landscapes: The business environment constantly evolves, with new challenges and opportunities arising regularly. Adapting lean principles to suit these changing landscapes is vital for sustained success. This involves being flexible and agile in applying lean concepts to different industries, business models, and customer demands. By embracing a culture of continuous improvement and remaining open to adjustments, organisations can ensure that lean remains relevant and effective in addressing the dynamic challenges they face.
Lean differs from traditional approaches by focusing on continuous improvement, customer value, and waste reduction. Unlike traditional methods prioritising mass production and excessive inventory, lean emphasises streamlined processes, pull-based production, and employee involvement. The lean approach aims to efficiently deliver high-quality products or services, adapt to customer demands, and eliminate non-value-adding activities to achieve sustainable success.
To successfully implement lean principles, organisations must undergo a cultural transformation involving all employees, from top management to frontline workers. Embracing lean principles and actively participating in the improvement process is essential. When executed efficiently, lean can revolutionise businesses by fostering a culture of continuous improvement, ultimately offering a competitive advantage in an ever-evolving business environment.
Start Free Trial
LEAN TRANSITION SOLUTIONS
The Old Vicarage, Pershore Road, Upton Snodsbury, Worcester, Worcestershire, WR7 4NR, United Kingdom.
Lean Transition Solution
-
Lean Industry 4.0 Solutions
- TITAN:Computerised Maintenance Management System
- Data Point:Computerised Balanced Scorecard
- Janus: Automated Shop-floor Data Capture System
- T-Card: Integrated Production Planning and Plant Level Execution System
- JDI: Maintenance Automation App
- Maximus: Integrated ERP System
- e-Contractor: Integrated In-house Contractor Management System
- Q-Point: Integrated Quality Management System
- Safety-Point: Integrated Health and Safety Management System
- Lean Assessment: Lean Audit and Assessment System
- Saisho: Lean 5S Audit and Assessment App
- Emergency Response App: To Manage Emergency Situations
-
Leadership 4.0 Solutions
- Your Career Academy(YCA): Learning and Development System
- YCA e-Learning : Management System
- MentorYou(MU): Mentoring App
- Leadership 4.0 : Leadership Transformation Program
- Lean Manufacturing Workshop
- Lean Manufacturing Consulting
- ILM Accredited Green Belt Training and Certification Program
- ILM Accredited Black Belt Training and Certification Program
- Software Development Service
- Resources
- Company
- Contact